Yes, after months of intense debate and delay, the U.S. Congress passed a major foreign aid package in April 2024, which President Biden signed into law. This package released approximately $61 billion in critical military, financial, and humanitarian assistance for Ukraine to help in its defense against Russia.
Have you been following the news and feeling confused about the status of U.S. aid to Ukraine? For months, it seemed like help was stuck, with headlines changing daily. Many people wondered if the support would ever arrive, leaving allies and Ukrainians in a state of uncertainty. This delay was a major source of global concern. But the wait is finally over.
This article will guide you through exactly what happened in simple, clear terms. We will break down what Congress passed, why it took so long, and what this aid means for Ukraine’s future. You will get the essential facts without the confusing political jargon. Let’s dive into the details of this historic decision.
The Long and Winding Road to Approval: Why Was the Aid Delayed?
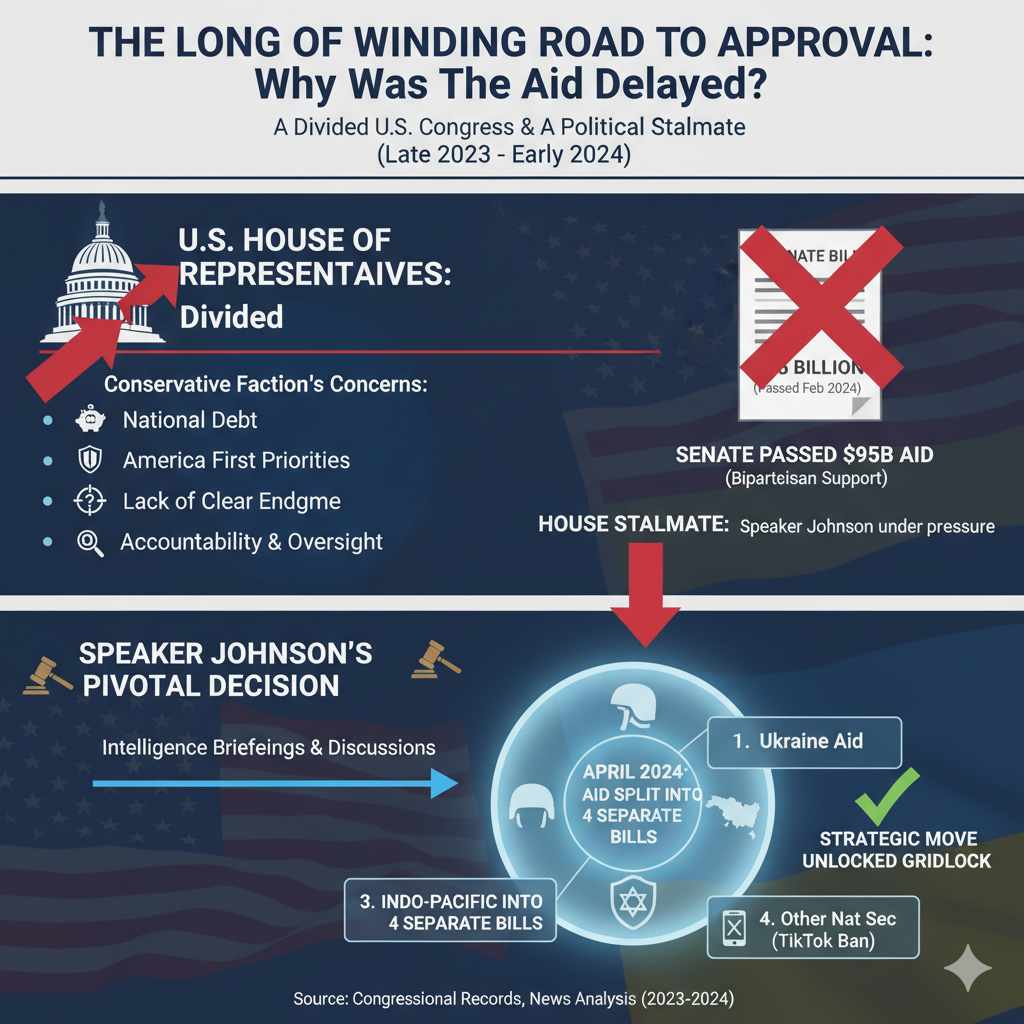
For much of late 2023 and early 2024, a crucial aid package for Ukraine was stalled in the U.S. Congress. While the need on the battlefield was urgent, political disagreements in Washington created a significant roadblock. Understanding this delay is key to grasping the full story.
A Divided House of Representatives
The primary reason for the hold-up was a deep division within the House of Representatives. The U.S. Senate, with strong bipartisan support, had passed a $95 billion national security bill in February 2024 that included aid for Ukraine, Israel, and Taiwan. However, the bill faced major opposition in the House.
A faction of Republican lawmakers, particularly the more conservative members, were hesitant to approve more funding for several reasons:
- Concerns over National Debt: Many argued that the U.S. could not afford to send tens of billions more overseas while facing a significant national debt.
- “America First” Priorities: Some representatives insisted that the government should prioritize domestic issues, especially security at the U.S.-Mexico border, before allocating funds to other nations.
- Lack of a Clear Endgame: There were questions about the long-term strategy in Ukraine and whether continued funding had a clear objective for ending the conflict.
- Calls for Accountability: Lawmakers demanded more oversight to ensure the aid was being used effectively and not lost to corruption.
These concerns created a political stalemate, as House Speaker Mike Johnson faced immense pressure from within his own party not to bring the Senate’s bill to a vote.
Speaker Johnson’s Pivotal Decision
For weeks, Speaker Johnson navigated a difficult political landscape. He was caught between the urgent pleas of international allies and the demands of his party’s conservative wing. After receiving intelligence briefings on the worsening situation in Ukraine and holding numerous discussions, he made a decisive move.
Instead of putting the single Senate bill up for a vote, he chose to split the aid into four separate bills:
- One providing aid to Ukraine.
- One for Israel.
- One for allies in the Indo-Pacific, including Taiwan.
- A fourth bill focused on other national security priorities, including a measure that could lead to a ban on TikTok.
This strategic decision allowed lawmakers to vote on each component individually, rather than forcing them to accept an all-or-nothing package. It proved to be the key that unlocked the legislative gridlock.
What’s Inside the Ukraine Aid Package? A Clear Breakdown
The aid package signed into law provides approximately $61 billion for Ukraine. However, this money is not just a blank check. It is allocated for specific purposes, primarily focused on military reinforcement, economic stability, and humanitarian relief. Understanding this breakdown shows how comprehensive the support is intended to be.
Here is a simplified look at how the funds are distributed. Note that these are approximate figures, as official allocations can be complex.
| Category of Aid | Approximate Amount (in Billions) | Primary Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Military & Defense Operations | $49.9 | Funding for weapons, ammunition, air defense systems, and replenishing U.S. military stocks of equipment sent to Ukraine. |
| Economic & Financial Assistance | $9.5 | Direct budget support to the Ukrainian government to help pay for essential services like pensions, salaries for first responders, and keeping the energy grid running. This portion is structured as a forgivable loan. |
| Humanitarian & Civilian Support | $1.6 | Funding for humanitarian needs, including assistance for refugees, food security, demining efforts, and addressing other civilian crises caused by the war. |
Military Support: The Critical Lifeline
The largest portion of the package is dedicated to military aid. This is the most urgent need, as Ukrainian forces were rationing ammunition and struggling to defend against relentless Russian attacks. The funding allows the U.S. to send a massive influx of essential equipment. According to the U.S. Department of Defense, this includes:
- Artillery Shells: 155mm and 105mm shells, which are fundamental for holding defensive lines.
- Air Defense Systems: Missiles for systems like the Patriot and NASAMS to protect cities and critical infrastructure from air strikes.
- Long-Range Missiles: The Army Tactical Missile System (ATACMS), which allows Ukraine to strike high-value targets far behind enemy lines.
- Armored Vehicles: Bradley Fighting Vehicles and other armored personnel carriers to support ground operations.
- Drones and Anti-Drone Systems: Crucial technology for modern warfare, used for both surveillance and attack.
A significant portion of this military funding, over $23 billion, is designated to replenish the U.S. military’s own stockpiles. This means that when the U.S. sends equipment to Ukraine, this money is used to manufacture new, often more advanced, replacements for American forces.
Economic and Financial Assistance
War is not just fought on the battlefield; it also requires a functioning government and economy. A key part of the aid package provides direct financial support to the Ukrainian government. This money is not for weapons but for keeping the country running. It ensures that teachers, doctors, and emergency workers can be paid, and that the government can continue to provide basic services to its citizens. This economic stability is vital for national morale and resilience.
How the Aid Bill Was Finally Passed: A Step-by-Step Look
The legislative process can be confusing, but the final passage of the Ukraine aid bill followed a clear, albeit dramatic, sequence of events. Here’s how it unfolded:
- The Senate Acts First: In February 2024, the Senate passed a single, comprehensive $95 billion national security package with a strong bipartisan vote of 70-29.
- Stalemate in the House: The bill was sent to the House of Representatives, where it stalled for over two months due to the political divisions mentioned earlier.
- Speaker Johnson’s Strategic Split: Facing a critical deadline, Speaker Mike Johnson restructured the aid into four separate bills to allow for individual votes.
- The House Passes the Bills: On April 20, 2024, the House held a rare Saturday session and passed all four bills with broad, bipartisan support. The Ukraine aid bill passed with a vote of 311-112.
- Back to the Senate: The House bills were combined back into a single package and sent to the Senate for a final vote.
- Final Senate Approval: On April 23, the Senate overwhelmingly approved the package with a 79-18 vote, demonstrating once again the strong bipartisan consensus in that chamber.
- Signed into Law: President Joe Biden signed the bill into law on April 24, officially releasing the funds and authorizing the immediate shipment of military aid.
What Happens Next? The Immediate Impact
The passage of the aid bill was not just a political victory; it had immediate, real-world consequences. The moment the bill was signed, the U.S. government and military began executing plans that had been in the works for weeks.
Rushing Supplies to the Front Lines
The Pentagon had pre-positioned weapons and ammunition in warehouses in Europe, primarily in Germany and Poland, in anticipation of the bill’s passage. Within hours of President Biden’s signature, the first shipments were on their way to Ukraine. The initial tranches of aid focused on the most critical needs: artillery shells, air defense interceptors, and other essential munitions. This rapid delivery was designed to help Ukrainian forces stabilize the front lines as quickly as possible.
A Boost for Morale and a Signal to the World
Beyond the physical supplies, the approval of U.S. aid sent a powerful message. For Ukrainian soldiers and civilians, it was a tremendous boost to morale, reaffirming that they were not abandoned by their most important ally. For Russia, it signaled that the U.S. and its partners were committed to supporting Ukraine for the long haul. For global allies, it demonstrated continued U.S. leadership and resolved on the world stage.

Understanding the Different Viewpoints
It’s important to recognize that the debate over Ukraine aid was complex, with valid arguments on both sides. Understanding these perspectives provides a fuller picture of the political dynamics at play. Here’s a summary of the main arguments for and against the aid package.
| Arguments FOR the Aid Package | Arguments AGAINST the Aid Package |
|---|---|
| Upholding International Law: Supporters argued that helping Ukraine defend itself is essential to deterring aggression and upholding the principle that sovereign borders cannot be changed by force. | Cost to U.S. Taxpayers: Opponents highlighted the immense cost, arguing that the money should be spent on domestic priorities like healthcare, infrastructure, or border security. |
| Weakening a U.S. Adversary: Many view the aid as a cost-effective way to degrade the military capabilities of Russia, a key strategic competitor, without risking American lives. | Risk of Escalation: Some feared that providing advanced, long-range weapons could provoke a wider conflict with Russia, potentially involving NATO. |
| Preventing a Wider Conflict: The belief is that if Russia succeeds in Ukraine, it may be emboldened to attack a NATO country, which would trigger a much larger and more dangerous war involving U.S. troops. | Lack of a Clear Strategy: Critics argued there was no clear vision for victory or a negotiated settlement, leading to fears of an endless “forever war.” |
| Strengthening U.S. Alliances: Providing aid reinforces U.S. commitments to its allies in Europe and around the world, strengthening partnerships and collective security. | Burden on European Allies: Some argued that European nations, being closer to the conflict, should bear a larger share of the financial burden for Ukraine’s defense. |
FAQ: Your Questions on Ukraine Aid Answered
Is the new U.S. aid to Ukraine a loan or a grant?
The majority of the aid, especially the military portion, is a grant. However, the $9.5 billion allocated for economic assistance was structured as a forgivable loan. This means the President has the authority to cancel repayment of the loan after November 2024, which is widely expected to happen. This was a compromise to gain support from some lawmakers concerned about the cost.
How much total aid has the U.S. given to Ukraine since the 2022 invasion?
With the passage of this new package, the total U.S. commitment to Ukraine since Russia’s full-scale invasion in February 2022 is approximately $175 billion. This includes military, financial, and humanitarian assistance. Authoritative sources like the Council on Foreign Relations provide detailed trackers of this support.
How soon did the new weapons and supplies arrive in Ukraine?
Very quickly. The U.S. military had supplies pre-staged in Europe, and the first shipments began moving within 24 hours of the bill being signed into law. Critical items like artillery shells and air defense missiles arrived at the front lines within days.
Why did it take Congress so long to approve this aid?
The delay was primarily due to political divisions in the House of Representatives. A group of lawmakers opposed further spending without linking it to other priorities, such as increased funding for U.S. border security. It took months of negotiation and a strategic decision by the House Speaker to break the legislative deadlock.
Does this aid package guarantee that Ukraine will win the war?
No, the aid package does not guarantee a victory. However, military and political experts agree that it is absolutely essential for Ukraine to continue its defense. It provides the necessary tools to stabilize the front lines, protect its cities, and prevent a military collapse. The outcome of the war still depends on many factors, including Ukraine’s strategy and the performance of its military.
Who in Congress voted for and against the aid?
The vote was bipartisan, meaning it received support from both Democrats and Republicans. In the House, 210 Democrats and 101 Republicans voted in favor, while 112 Republicans voted against it. In the Senate, the support was even more broadly bipartisan, with leaders from both parties voting yes.
How does the U.S. ensure the aid is not lost to corruption?
The U.S. government has several oversight mechanisms in place. These include teams from the Department of Defense, the State Department, and USAID on the ground in Ukraine to monitor the distribution and use of aid. The legislation itself also includes requirements for monitoring and reporting to ensure accountability and transparency.
Conclusion: A Decisive Moment for Ukraine and Its Allies
The passage of the $61 billion aid package marks a pivotal moment in the war in Ukraine. After a long and uncertain delay that cast doubt on the future of Western support, the United States delivered a resounding confirmation of its commitment. This infusion of weapons, ammunition, and financial support provides Ukraine with the critical resources it needs to defend its sovereignty, protect its people, and push back against aggression.
While the road ahead remains incredibly challenging, this aid provides a vital lifeline. It stabilizes the front lines, boosts morale, and sends a clear signal that the democratic world will not stand by while a sovereign nation is under attack. The decision made by Congress in April 2024 will be remembered as a crucial turning point, one that gave Ukraine a fighting chance to determine its own future.

