Yes, President Trump eventually released the military aid to Ukraine on September 11, 2019. However, the aid was withheld for 55 days, a delay that became the central focus of his first impeachment inquiry. The timeline reveals a complex story of political pressure, official concerns, and the eventual release of the funds.
The story of U.S. aid to Ukraine in 2019 can feel confusing. It was a major news event filled with complicated terms and fast-moving developments. You might remember hearing about a phone call, an impeachment, and a debate over military funding, but the details can be hard to track. It’s a common feeling, and many people were left wondering what really happened.
Don’t worry. This article will break it all down for you. We will walk through the events step-by-step, using a simple timeline to explain what happened, when it happened, and why it became so important. You will get a clear picture of the entire situation, from the initial hold on the aid to its final release and the consequences that followed.
What Was the Ukraine Aid and Why Did It Matter?
Before we dive into the timeline, it’s helpful to understand what this aid was for. In 2019, Congress approved nearly $400 million in security assistance for Ukraine. This was not a controversial decision at the time. In fact, it had strong support from both Democrats and Republicans.
This money was meant to help Ukraine defend itself. Since 2014, Ukraine has been in a conflict with Russia-backed separatists in the eastern part of the country. The aid package included funds for things like:
- Military training
- Equipment, such as sniper rifles and rocket-propelled grenade launchers
- Logistical support
- Naval assets to defend its coastline
For Ukraine, this aid was a critical symbol of American support. It showed that the United States stood with them in their fight to remain a sovereign nation. For U.S. foreign policy, supporting Ukraine was seen as a way to push back against Russian aggression in Eastern Europe. The delay of this aid, therefore, was a very big deal for officials in both countries.

A Step-by-Step Timeline of the Withheld Aid
The decision to hold the aid was not a single event but a series of actions and conversations that took place over several months. Here is a clear breakdown of the key moments that led to the freeze and its eventual release.
May 2019: Early Signs and a Canceled Trip
In May 2019, Ukraine inaugurated its new president, Volodymyr Zelenskyy, a former comedian who ran on an anti-corruption platform. Vice President Mike Pence was scheduled to lead the U.S. delegation to the inauguration, a signal of strong American support.
However, President Trump instructed Pence not to go. Around the same time, Trump’s personal lawyer, Rudy Giuliani, was publicly calling for Ukraine to investigate Joe Biden, who was emerging as a top contender for the 2020 Democratic presidential nomination. These early events set the stage for the pressure campaign that would follow.
July 2019: The Aid is Officially Frozen
Things escalated in July. On July 18, 2019, the White House Office of Management and Budget (OMB) officially placed a hold on the military aid to Ukraine. This order prevented the Department of Defense from sending the funds that Congress had already approved.
Officials within the administration were confused and concerned. Many testified later that they were not given a clear reason for the hold. They knew the aid was vital for Ukraine’s security and that withholding it could send a dangerous message to Russia.
July 25, 2019: The “Perfect” Phone Call
Just one week after the aid was frozen, President Trump had a phone call with Ukrainian President Zelenskyy. This call would later become the centerpiece of the impeachment inquiry. During the call, Trump raised two key issues:
- A debunked theory about the 2016 election: He asked Zelenskyy to look into a conspiracy theory involving a server from the Democratic National Committee.
- The Bidens: Trump explicitly asked Zelenskyy to “look into” former Vice President Joe Biden and his son, Hunter Biden, who had served on the board of a Ukrainian energy company called Burisma.
Trump told Zelenskyy that the United States had been “very, very good to Ukraine” and then immediately asked him to “do us a favor though” before mentioning the investigations. This sequence of comments led Democrats to accuse him of using the withheld aid as leverage—a “quid pro quo.”
August 2019: A Whistleblower Steps Forward
Throughout August, the aid remained frozen. U.S. diplomats and national security officials grew increasingly alarmed. They felt that the president was using foreign policy for personal political gain, which could damage national security.
On August 12, 2019, an anonymous intelligence official filed a formal whistleblower complaint. The complaint detailed concerns about the July 25 phone call and the broader effort to pressure Ukraine. This complaint set in motion a chain of events that would make the entire affair public.
September 2019: Public Pressure and the Release
By early September, news of the withheld aid began to leak to the public. Members of Congress from both parties started asking questions and demanding that the administration release the funds. Three key House committees launched an investigation into the matter.
Facing intense pressure from Congress and a growing public scandal, the White House finally relented. On September 11, 2019, the administration lifted the hold, and the aid was released to Ukraine. The hold had lasted for 55 days.
Key Dates in the Ukraine Aid Saga
This table provides a quick-glance summary of the most important events in the timeline.
| Date | Event | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| May 2019 | VP Pence’s trip to Ukraine is canceled. | An early signal of shifting U.S. policy and pressure. |
| July 18, 2019 | The White House OMB officially freezes the aid. | The nearly $400 million in congressionally approved funds are formally blocked. |
| July 25, 2019 | Trump-Zelenskyy phone call takes place. | Trump asks for investigations into political rivals, a key part of the impeachment case. |
| August 12, 2019 | A whistleblower complaint is filed. | This formal complaint triggers an official review and eventually leads to public disclosure. |
| September 11, 2019 | The hold is lifted and aid is released. | The funds are finally sent to Ukraine after 55 days, amid growing public and congressional pressure. |
Why Was the Aid Withheld? The Two Competing Stories
There are two very different explanations for why the Trump administration decided to freeze the aid to Ukraine. Understanding both is key to understanding the controversy.
The Official White House Explanation
President Trump and his supporters offered several reasons for the hold. The main arguments were:
- Concerns about corruption: They claimed they wanted to ensure that Ukraine’s new government was serious about fighting the corruption that had long plagued the country.
- Burden-sharing: They argued that European countries were not paying their fair share to support Ukraine and that the U.S. shouldn’t carry the financial burden alone.
However, many officials, including those in the Department of Defense, had already certified that Ukraine had met the necessary anti-corruption benchmarks to receive the aid. This made the official explanation seem questionable to critics.
The Impeachment Allegation: A Quid Pro Quo
The other explanation formed the basis of the impeachment inquiry against President Trump. This view alleges that the aid was withheld as leverage to pressure President Zelenskyy into announcing investigations that would benefit Trump’s 2020 reelection campaign.
This is often called a “quid pro quo,” a Latin phrase that means “this for that.” The allegation was that Trump was offering the military aid (the “this”) in exchange for the announcement of politically motivated investigations (the “that”). Key witnesses in the impeachment inquiry, including high-ranking diplomats and national security officials, testified that they believed this was the case.
Comparing the Two Explanations
To make it even clearer, here is a table comparing the different motivations presented for the hold.
| Explanation | Core Argument | Evidence Cited by Proponents |
|---|---|---|
| Official White House Stance | The hold was about fighting corruption and getting allies to pay more. | President Trump’s public statements about corruption and European contributions. |
| Impeachment Allegation | The hold was leverage to get Ukraine to investigate the Bidens. | The transcript of the July 25 call, testimony from officials, and the timing of the hold. |
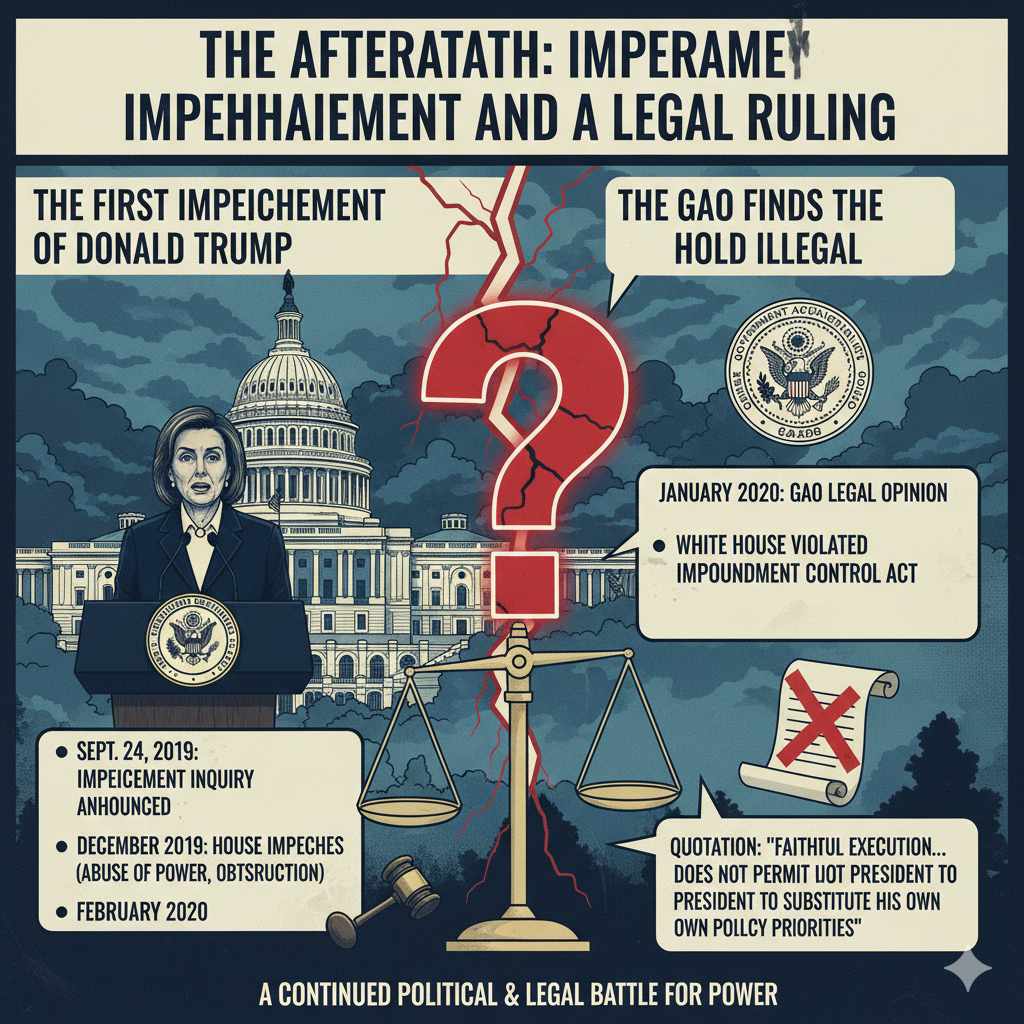
The Aftermath: Impeachment and a Legal Ruling
The release of the aid on September 11 did not end the controversy. In fact, it was just the beginning of a major political battle in Washington.
The First Impeachment of Donald Trump
On September 24, 2019, House Speaker Nancy Pelosi announced a formal impeachment inquiry. The inquiry focused on whether President Trump had abused his power by using the office of the presidency to solicit interference from a foreign country in the 2020 U.S. election.
In December 2019, the House of Representatives voted to impeach President Trump on two articles: abuse of power and obstruction of Congress. The case then moved to the Senate for a trial. In February 2020, the Senate, where Republicans held the majority, voted to acquit Trump on both charges. This meant he was not removed from office.
The GAO Finds the Hold Illegal
While the impeachment trial was political, there was also a legal review of the aid hold. The Government Accountability Office (GAO), a non-partisan government watchdog, investigated the matter. In January 2020, the GAO released a legal opinion concluding that the White House’s hold on the Ukraine aid was illegal.
The GAO found that the OMB violated the Impoundment Control Act, a law that limits the president’s ability to withhold funds that Congress has appropriated. The report stated, “Faithful execution of the law does not permit the President to substitute his own policy priorities for those that Congress has enacted into law.” This finding provided legal weight to the argument that the administration had overstepped its authority, separate from the political motivations behind the hold.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. So, did Ukraine ever get the money?
Yes, all the aid was eventually delivered to Ukraine. The hold was lifted on September 11, 2019, and the funds were released. The issue was not that the aid was canceled, but that it was delayed and the reasons for that delay.
2. What exactly is a “quid pro quo”?
A quid pro quo is a Latin phrase that means “something for something” or “this for that.” In this context, it refers to the allegation that President Trump was offering something (the military aid and a White House meeting) in exchange for something he wanted (investigations into his political rivals).
3. Who was the whistleblower?
The whistleblower was a member of the U.S. intelligence community. Their identity has been kept confidential to protect them from retaliation, as is standard practice under whistleblower protection laws. Their role was to report a concern of “urgent” wrongdoing through official channels, which they did.
4. Why was investigating the Bidens so important?
At the time, Joe Biden was the front-runner for the Democratic nomination to run against President Trump in the 2020 election. An investigation into his son, Hunter, and his work in Ukraine could have created a political scandal and potentially harmed Biden’s campaign.
5. Did the 55-day delay hurt Ukraine?
While it’s difficult to measure the exact military impact, national security experts and diplomats argued that the delay sent a dangerous message. It created uncertainty about American support at a time when Ukraine was facing active aggression from Russia. This could have emboldened Russia and weakened Ukraine’s negotiating position.
6. What does it mean to be impeached but not removed from office?
The U.S. Constitution sets up a two-step process. The House of Representatives has the power to impeach, which is like a formal indictment or accusation of wrongdoing. If the House votes to impeach, a trial is then held in the Senate. It takes a two-thirds vote in the Senate to convict and remove a president from office. In President Trump’s case, the House impeached him, but the Senate did not convict him.
Conclusion: A Complex Story with Lasting Impact
So, did President Trump release the aid to Ukraine? The simple answer is yes, he did. But the full story is far more complex. The aid was released only after a 55-day hold, during which President Trump and his associates pressured Ukraine to investigate his political rivals. This timeline of events led to a whistleblower complaint, a major public scandal, and ultimately, the third presidential impeachment in U.S. history.
While the Senate acquitted him, the controversy left a lasting mark on American politics and foreign policy. It raised fundamental questions about the limits of presidential power, the integrity of elections, and the role of the United States as a reliable ally on the world stage. Understanding this timeline is not just about revisiting a past political battle; it is about grasping a key moment that shaped modern American history.

