Yes, State Department and Pentagon officials confirmed Ukraine met all anti-corruption requirements and repeatedly tried to release Congressionally-approved military aid. However, the aid was withheld by the White House’s Office of Management and Budget (OMB) from July to September 2019, a decision that became central to a presidential impeachment inquiry.
News about government actions can be confusing. You may have heard about a hold on U.S. aid to Ukraine and wondered what really happened. Many reports mentioned different government departments, making it hard to follow the facts. It is easy to get lost in the details.
This article breaks it down with simple, proven facts. We will look at the State Department’s role and explain step-by-step what occurred during the 2019 hold on military aid. You will get a clear picture of how the process works and who was responsible for the delay. Let’s explore the essential facts together.
Understanding U.S. Aid to Ukraine: What Is It?
Before diving into the events of 2019, it’s helpful to know what U.S. aid to Ukraine is and why it exists. The United States provides support to Ukraine for several important reasons. A key goal is to help Ukraine defend its sovereignty and territorial integrity, especially after Russia’s invasion in 2014. Aid also helps Ukraine strengthen its democracy and reduce corruption.
This support generally falls into three main categories:
- Security and Military Assistance: This is the aid that gets the most attention. It includes funding for weapons, training for Ukrainian soldiers, and equipment like night-vision goggles, counter-artillery radar, and patrol boats. The goal is to help Ukraine’s military better defend itself.
- Economic and Development Assistance: This aid helps stabilize Ukraine’s economy. It supports things like energy sector reform, private sector growth, and building a stronger market economy. A stable economy is crucial for a country’s overall strength.
- Humanitarian Assistance: This aid provides essential relief to people affected by the conflict. It includes food, shelter, safe drinking water, and medical care for those displaced from their homes or living in conflict zones.
The specific aid at the center of the 2019 controversy was about $391 million in security assistance. This money was approved by the U.S. Congress with bipartisan support. For the aid to be released, the Department of State and the Department of Defense had to certify that Ukraine was making enough progress in fighting corruption. This is a standard requirement to ensure U.S. taxpayer money is used responsibly.

The 2019 Hold on Military Aid: A Timeline of Key Events
The story of the hold on military aid unfolded over several months in 2019. Understanding the timeline is key to seeing how events played out and who was involved. Here is a step-by-step breakdown based on official records and testimony.
- May 23, 2019: Top U.S. officials, including those from the State Department and Department of Defense, met with President Trump after attending the inauguration of Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy. They recommended the U.S. show strong support for the new president. According to testimony, President Trump expressed skepticism about Ukraine and instructed them to “talk to Rudy,” referring to his personal lawyer, Rudy Giuliani.
- June 18, 2019: The Department of Defense publicly announced its plan to provide $250 million in security assistance to Ukraine. This was part of the total aid package approved by Congress.
- Mid-July 2019: Behind the scenes, officials at the Office of Management and Budget (OMB), which is part of the White House, communicated a hold on the aid. State and Defense Department officials were surprised, as they had already certified that Ukraine had met the necessary anti-corruption benchmarks.
- July 25, 2019: President Trump had a phone call with Ukrainian President Zelenskyy. A memo of this call later revealed that President Trump asked Zelenskyy for a “favor” to investigate a political rival and a debunked theory about the 2016 election.
- August 2019: News of the hold on military aid began to leak to the public. U.S. diplomats and officials became increasingly concerned. William Taylor Jr., the top U.S. diplomat in Ukraine, texted other officials that it was “crazy to withhold security assistance for help with a political campaign.”
- September 11, 2019: After intense pressure from Congress, diplomats, and the public, the White House released the hold on the aid. The funding was finally allowed to move forward.
- September 24, 2019: The U.S. House of Representatives launched a formal impeachment inquiry into President Trump’s actions regarding Ukraine. The inquiry focused on whether he abused his power by withholding the aid to pressure a foreign government for personal political gain.
This timeline shows that the official government agencies responsible for the aid, like the State Department, were prepared to send it. The delay was directed from outside these departments.
Who Was Involved? Key Players and Their Roles
Many individuals and government agencies played a part in this story. Knowing who they are and what they did helps clarify the situation. The main players were spread across the State Department, the Department of Defense, and the White House.
Here is a table outlining the key figures and their roles in the aid process:
| Name / Agency | Role / Title at the Time | Involvement in the Aid Process |
|---|---|---|
| Donald Trump | President of the United States | Ordered the hold on the aid and asked the Ukrainian President for investigations. |
| Mike Pompeo | Secretary of State | As head of the State Department, he was aware of the hold and involved in communications with Ukrainian officials. |
| William (Bill) Taylor Jr. | Acting Ambassador to Ukraine | The top U.S. diplomat in Kyiv. He raised serious alarms about the aid hold through official channels. |
| George Kent | Deputy Assistant Secretary of State | A senior State Department official who testified that the push for political investigations undermined U.S. foreign policy. |
| Office of Management and Budget (OMB) | White House Agency | Placed the formal holds on the aid at the direction of the President, preventing the funds from being spent. |
| Department of Defense (DoD) | U.S. Military Leadership | Along with the State Department, it certified that Ukraine had met the necessary reform requirements to receive the aid. |
The State Department’s Role: Efforts to Release the Aid
The central question is what the State Department did. Did it try to release the aid? The proven facts from official testimony and documents show a clear answer: yes, they did.
Career officials at the State Department, along with their counterparts at the Department of Defense, had done the work required by law. They analyzed Ukraine’s progress on reforms and formally certified that the country was eligible for the aid. This certification was a legal prerequisite for sending the money.
Once the hold was put in place by the OMB, many State Department officials began working to get it lifted. Here’s what their efforts looked like:
- Formal Meetings and Memos: Officials repeatedly raised the issue in interagency meetings. They argued that withholding aid weakened Ukraine in its conflict with Russia and damaged U.S. credibility.
- Diplomatic Cables: Diplomats like Ambassador Bill Taylor sent cables back to Washington D.C. expressing grave concerns. These official communications are a formal way for ambassadors to report problems and recommend actions.
- Direct Testimony: During the impeachment inquiry, numerous State Department officials testified under oath. They described a consistent effort by career professionals to follow the law and release the aid. For example, George Kent stated that the push for politically motivated investigations was “injurious to the rule of law” and U.S. national security interests.
These actions show a clear pattern. The professional staff and leadership within the State Department’s European bureau were aligned with the policy set by Congress: to support Ukraine. The hold was not their decision. Instead, it was an order from the White House that they had to follow, even while many of them disagreed with it and worked to reverse it. The U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO), a non-partisan watchdog, later issued a legal decision stating that the OMB’s hold on the aid was, in fact, illegal. You can read more about the GAO’s findings on their official website, gao.gov.
Why Was the Aid Withheld? The Official and Unofficial Reasons
There were two competing explanations for why the aid was withheld. Understanding both is crucial to grasping the full picture.
The Official Reason
The official reason given by the White House at the time was concern over corruption in Ukraine. The administration argued it wanted to be sure that the new Ukrainian government under President Zelenskyy was serious about fighting corruption before sending hundreds of millions of U.S. taxpayer dollars. They also mentioned wanting European allies to contribute more to Ukraine’s defense.
However, this explanation was contradicted by the actions of the State and Defense Departments. These agencies had already formally certified that Ukraine had made significant progress on anti-corruption reforms, meeting the legal standard set by Congress.
The Unofficial Reason
The impeachment inquiry uncovered a different, unofficial reason. Testimony from numerous officials, including Ambassador to the E.U. Gordon Sondland, revealed that the aid was being held as leverage. The goal was to pressure President Zelenskyy into publicly announcing investigations into two specific matters:
- Burisma Holdings: A Ukrainian energy company where Hunter Biden, the son of then-presidential candidate Joe Biden, had served on the board.
- The 2016 Election: A debunked conspiracy theory that Ukraine, not Russia, had interfered in the 2016 U.S. presidential election.
Officials testified that there was a clear “quid pro quo” (a favor for a favor) being communicated to the Ukrainians: the military aid and a White House meeting for President Zelenskyy in exchange for announcing these investigations. This use of foreign policy for personal political benefit was the core of the abuse of power charge in the impeachment of President Trump.
You can find extensive documentation and testimony related to the inquiry at the official U.S. Congress website, such as through the congress.gov portal, which archives official proceedings and reports.
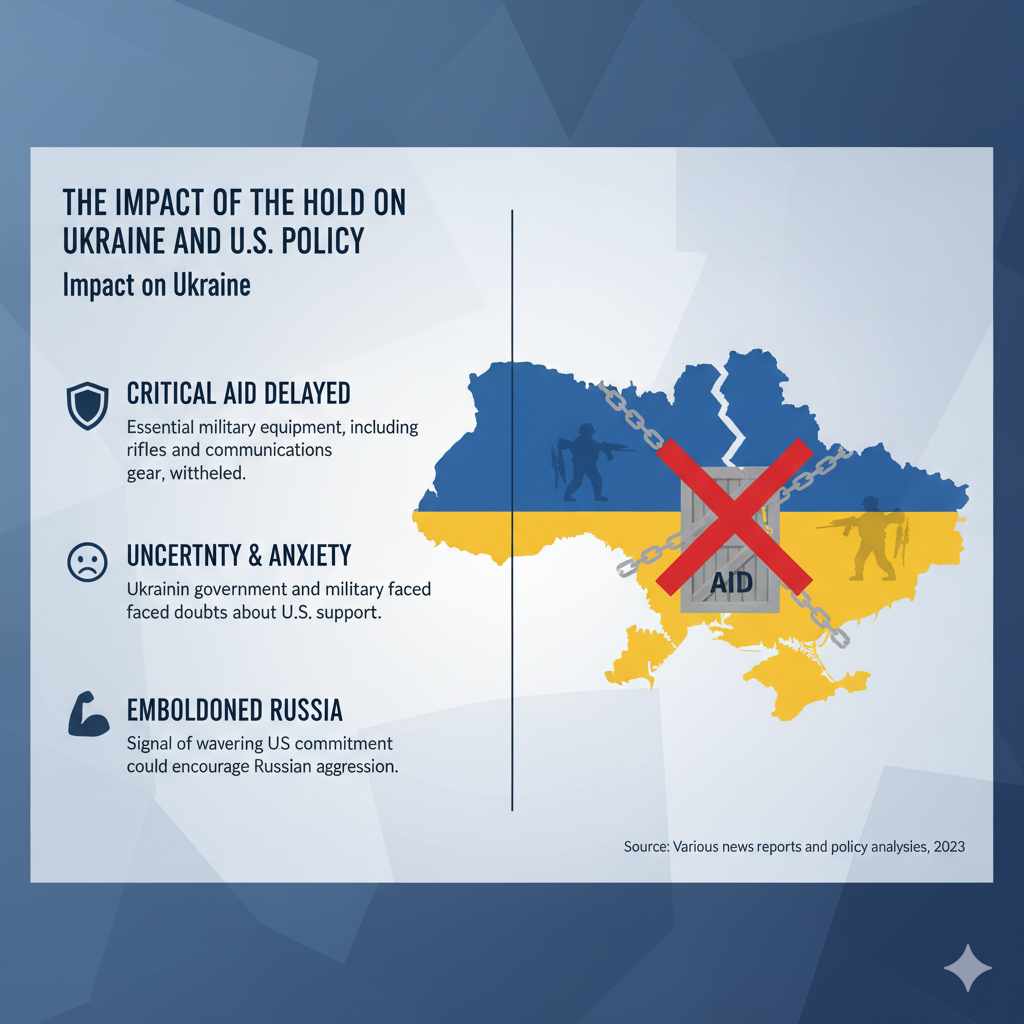
The Impact of the Hold on Ukraine and U.S. Policy
The nearly two-month hold on security assistance was not just a political dispute in Washington. It had real-world consequences for Ukraine and for the standing of the United States.
Impact on Ukraine
For Ukraine, the aid was critical. The country was in an active war with Russian-backed forces in its eastern Donbas region. The U.S. aid provided essential military equipment, including items that Ukraine’s own defense industry could not produce. The delay created uncertainty and anxiety within the Ukrainian government and military. Soldiers on the front lines were waiting for resources like sniper rifles and communications gear. The hold sent a signal that U.S. support might be wavering, which could embolden Russia.
Impact on U.S. Foreign Policy
For the United States, the incident raised serious questions about the reliability of its foreign policy commitments. Key impacts included:
- Damaged Credibility: Allies and adversaries around the world watched as Congressionally-approved aid was held up for what appeared to be political reasons. This made it harder for U.S. diplomats to be seen as credible and for the U.S. to be trusted as a reliable partner.
- Politicization of Foreign Aid: The incident set a dangerous precedent of using foreign aid, which is a tool of national security, for personal political objectives. This can undermine the goals of the aid and harm long-term U.S. interests.
- Internal Division: The episode created deep divisions within the U.S. government. Career diplomats and national security professionals were put in a position where their professional judgment and the official policy of the United States were being overridden for reasons outside of established foreign policy goals.
Ultimately, the aid was released, but the damage to trust and policy norms had already been done.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the State Department?
The U.S. Department of State, often just called the State Department, is the executive department responsible for the nation’s foreign policy and international relations. It is led by the Secretary of State and manages U.S. embassies and consulates around the world.
2. How much aid was held up in 2019?
The total amount of security assistance withheld was approximately $391 million. This included $250 million from the Department of Defense’s Ukraine Security Assistance Initiative and $141 million from the State Department’s Foreign Military Financing program.
3. Was the aid eventually released?
Yes. On September 11, 2019, the White House lifted the hold, and the aid was released. However, the delay itself became the subject of major controversy and an impeachment inquiry.
4. Why is U.S. aid to Ukraine so important?
U.S. aid is critical for helping Ukraine defend itself against Russian aggression. It strengthens Ukraine’s military, supports its economy, and promotes democratic reforms. A strong, independent Ukraine is seen as vital to stability in Europe and a key U.S. foreign policy interest.
5. Did the State Department have the final say on the aid?
No. While the State Department and the Pentagon recommended releasing the aid after certifying Ukraine had met its obligations, the final decision to place a hold came from the White House. This was executed through the Office of Management and Budget (OMB).
6. What is the Office of Management and Budget (OMB)?
The OMB is the largest office within the Executive Office of the President of the United States. Its primary function is to produce the president’s budget, but it also measures the quality of agency programs, policies, and procedures to see if they comply with the president’s policies.
7. Was withholding the aid found to be illegal?
Yes. In January 2020, the Government Accountability Office (GAO), a non-partisan government watchdog, issued a legal opinion stating that the White House’s hold on the aid violated the Impoundment Control Act. The law requires the executive branch to spend funds as appropriated by Congress.
Conclusion
The story of the 2019 hold on military aid to Ukraine can seem complicated, but the proven facts offer a clear picture. The U.S. State Department, along with the Department of Defense, fulfilled its legal duty by certifying that Ukraine was eligible for the aid. Career officials and diplomats consistently advocated for its release, arguing it was vital for both Ukrainian security and U.S. national interests.
The decision to withhold the aid did not come from these departments. Instead, it was a directive from the White House, executed by the OMB, and linked to a desire for investigations into political rivals. While the aid was eventually released, the incident highlighted the tensions between established foreign policy processes and political pressures.
Understanding these events is not about taking a political side; it is about knowing how government works and the importance of following established laws and procedures. The facts show that the professionals at the State Department tried to get the aid to Ukraine as Congress intended.

